Dining Philosophers Problem In Os Mcq

Computer science mca operating system.
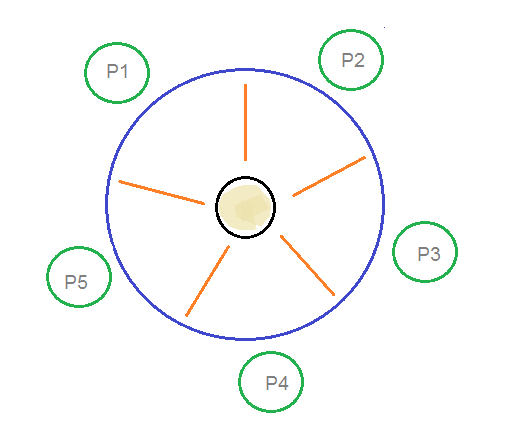
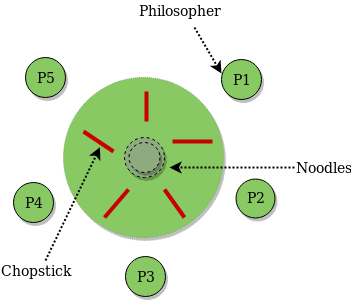
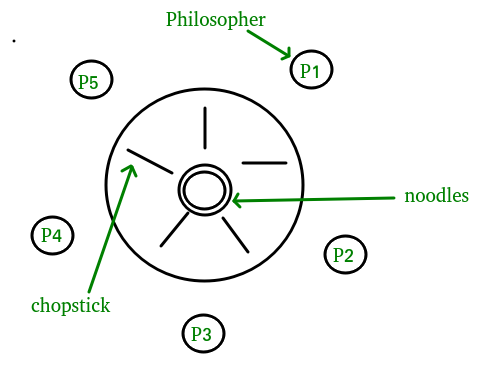
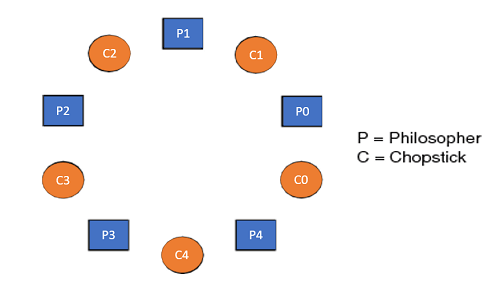
Dining philosophers problem in os mcq. The dining philosopher s problem is the classical problem of synchronization which says that five philosophers are sitting around a circular table and their job is to think and eat alternatively. There is one chopstick between each philosopher. The bounded buffer problem is also known as a readers writers problem b dining philosophers problem c producer consumer problem d none of the mentioned view answer. The dining table has five chopsticks and a bowl of rice in the middle as shown in the below figure.
This set of 1000 operating system mcqs focuses on the classic synchronization problems 1. It was originally formulated in 1965 by edsger dijkstra as a student exam exercise presented in terms of computers competing for access to tape drive peripherals. When a philosopher wants to eat he uses two chopsticks one from their left and one from their right. The dining philosophers problem is another classic synchronization problem which is used to evaluate situations where there is a need of allocating multiple resources to multiple processes.
There is a bowl of rice for each of the philosophers and 5 chopsticks. Above program is a monitor solution to the dining philosopher problem. We are now in a position to describe our solution to the dining philosophers problem. Entities noodles rice chopstics philosophers imagine five philosophers sitting around circular table and have a bowl of rice or noodles in the middle and there are five.
A there are n philosophers spending their lives thinking and eating in a room. The dining philosophers problem states that there are 5 philosophers sharing a circular table and they eat and think alternatively. In their round table there is a plate of infinite rice and n chopsticks. Os the dining philosophers problem a a.
This allows philosopher i to delay herself when she is hungry but is unable to obtain the chopsticks she needs. He tries to pick up the two chopsticks that are on his right and his left. At any instant a philosopher is either eating or thinking. We also need to declare.
A philosopher may eat if he can pickup the two chopsticks adjacent to him. The dining philosophers problem. A hungry philosopher may only eat if. From time to time a philosopher gets hungry.
In computer science the dining philosophers problem is an example problem often used in concurrent algorithm design to illustrate synchronization issues and techniques for resolving them. Prerequisite process synchronization semaphores dining philosophers solution using monitors the dining philosopher problem the dining philosopher problem states that k philosophers seated around a circular table with one chopstick between each pair of philosophers. A philosopher needs both their right and left chopstick to eat. A bowl of noodles is placed at the center of the table along with five chopsticks for each of the philosophers.