Dining Philosophers Problem In Os Program In C

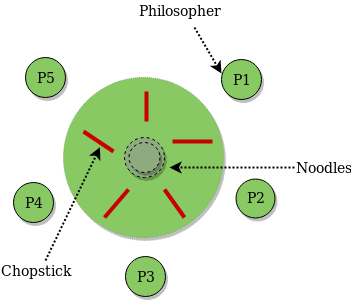
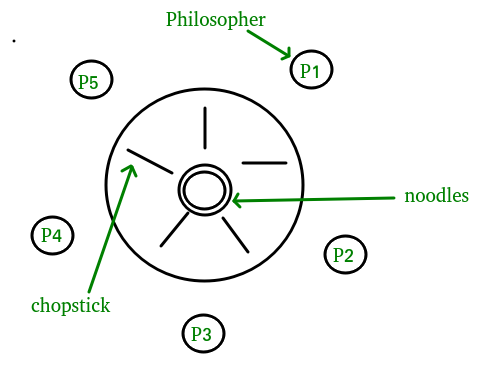
Five silent philosophers sit around table with a bowl of spaghetti.
Dining philosophers problem in os program in c. Program for dining philosophers problem in c. A fork is placed between each pair of adjacent philosophers. Os the dining philosophers problem a a. In an operating system a deadlock occurs when a process or thread enters a waiting state because a requested system resource is held by another waiting process which in turn is waiting for another resource held.
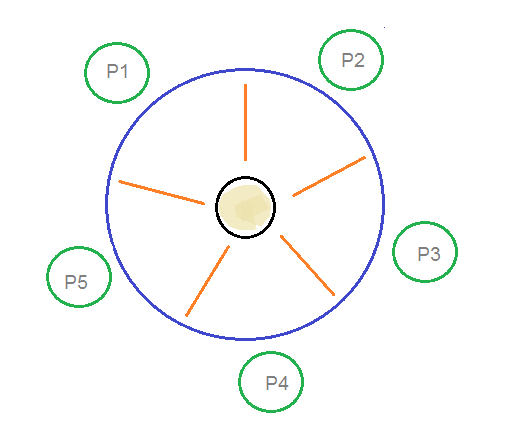
A there are n philosophers spending their lives thinking and eating in a room. A philosopher may eat if he can pickup the two chopsticks adjacent to him. Among them one particular question caught my attention. The dining philosophers scenario.
Now let us discuss the problem. Suppose there are n philosophers meeting around a table eating spaghetti and talking about philosophy. Same problem but instead of philosophers processes are there and instead of forks resources are there. The dining philosophers problem is another classic synchronization problem which is used to evaluate situations where there is a need of allocating multiple resources to multiple processes.
There is a bowl of rice for each of the philosophers and 5 chopsticks. Write a c program to solve dining philosophers problem dining philosophers problem is a classic synchronization problem a problem introduced by dijkstra concerning resource allocation between processes. It is the dining philosophers problem. We follow above solution to avoid dead lock condition.
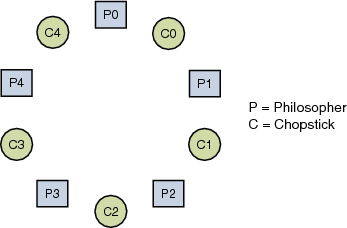
There are only n forks available such that only one fork between each philosopher. A philosopher needs both their right and left chopstick to eat. The dining philosophers problem states that there are 5 philosophers sharing a circular table and they eat and think alternatively. In their round table there is a plate of infinite rice and n chopsticks.
From time to time a philosopher gets hungry. There is one chopstick between each philosopher. In operating system this concept used in process synchronization.