Dining Philosophers Problem Solution Using Semaphores In Os

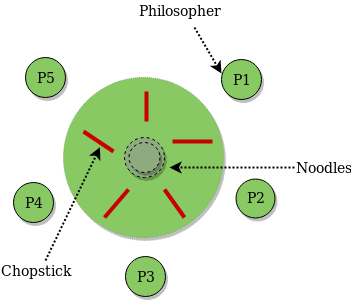
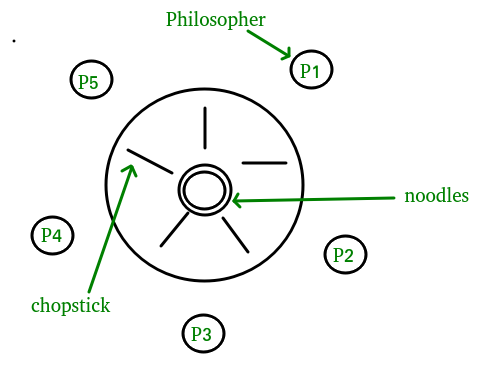
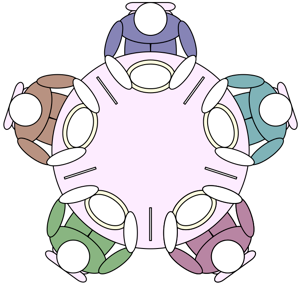
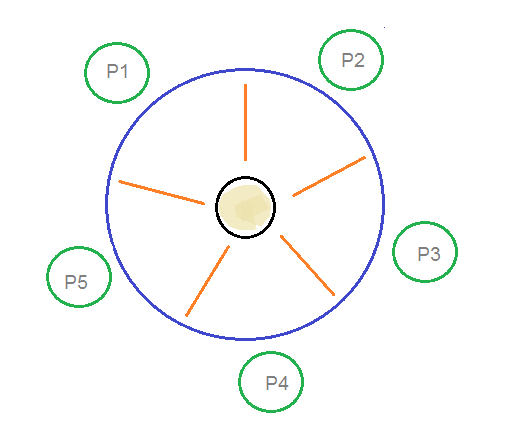
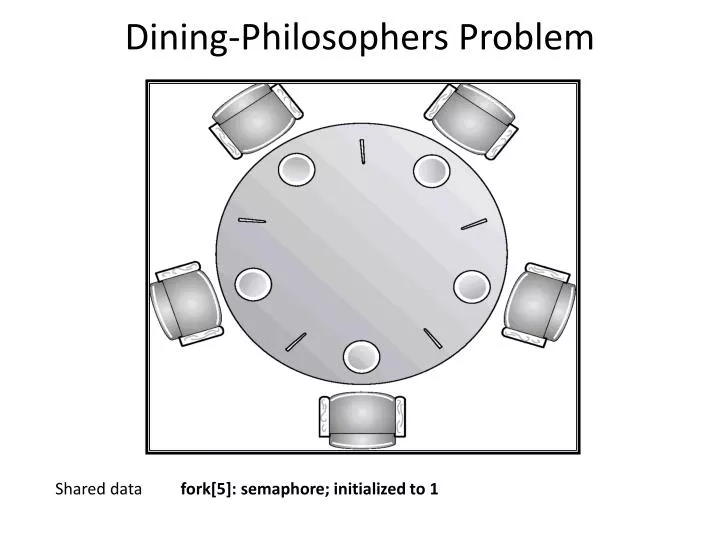
Prerequisite process synchronization semaphores dining philosophers solution using monitors the dining philosopher problem the dining philosopher problem states that k philosophers seated around a circular table with one chopstick between each pair of philosophers.
Dining philosophers problem solution using semaphores in os. A philosopher can be in anyone of the three. Each philosopher is a process. Some ways to avoid deadlock are. A philosopher may eat if he can pickup the two chopsticks adjacent to him.
The fork and the spaghetti are not part of the monitor. Output shows the various stages that each philosopher passes through within a certain time. Below is my code. There is one chopstick between each philosopher.
All philosophers decide to eat at the same time and all pick up their left chopstick first and or starvation. I am trying to solve the dining philosophers problem using semaphores in c. Use an array of semaphores chopstick 0 4 all initialized to 1. Prerequisite process synchronization semaphores dining philosophers solution using monitors the dining philosopher problem the dining philosopher problem states that k philosophers seated around a circular table with one chopstick between each pair of philosophers.
This is somewhat like an abstract problem in a novel dimension. To implement dining philosophers problem using threads and mutex. The dining philosopher is a classic synchronization problem as it demonstrates a large class of concurrency control problems. A philosopher may eat if he can pickup the two chopsticks adjacent to him.
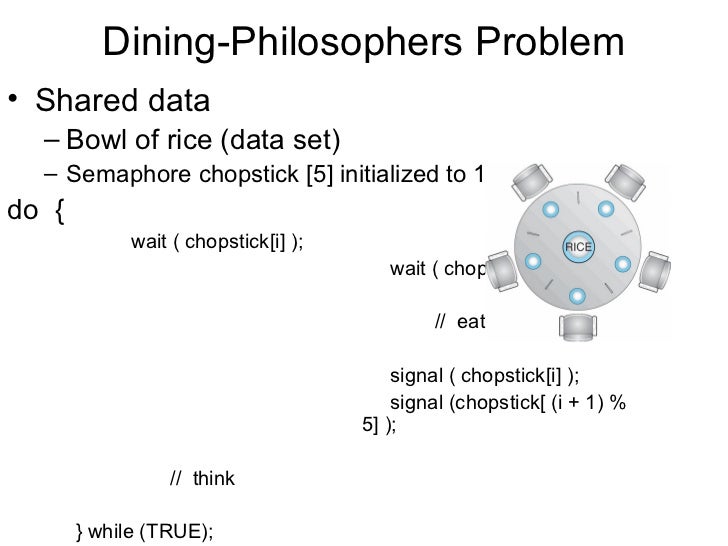
The pseudocode can be given as. The input to the program is the number of philosophers to be seated around the table. The usage of semaphores is very similar to using mutex locks. Each semaphore is initialized to a number indicating how many resources associated with that semaphore are available at that.
A solution of the dining philosophers problem is to use a semaphore to represent a chopstick. Problem description develop a program to implement the solution of the dining philosopher s problem using threads. That is why i set dt to 4. A monitor is used to control access to state variables and condition variables.
Dining philosophers problem using semaphores. The dining philosophers problem is another classic synchronization problem which is used to evaluate situations where there is a need of allocating multiple resources to multiple processes. Sometimes when it comes to computers some of the analogous situations often demands solutions in a creative fashion. Instead of the binary operation in mutex locks holding lock releasing lock semaphores function on the idea of number of resources.
Solution of dining philosophers problem using semaphores. There is one chopstick between each philosopher. Can suffer from deadlock e g. This can be implemented using a semaphore initialized to n 1 value where n is the number of philosophers present.