Explain Dining Philosophers Problem In Os
In computer science the dining philosophers problem is an example problem often used in concurrent algorithm design to illustrate synchronization issues and techniques for resolving them.
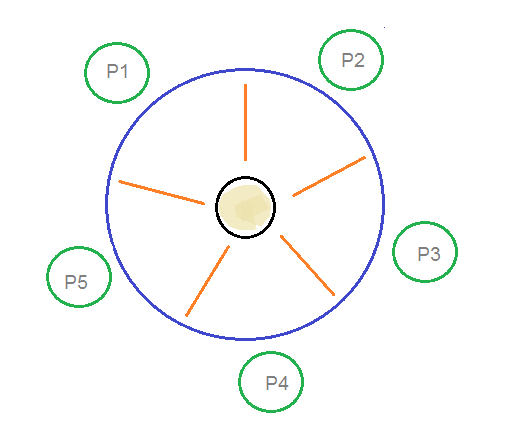
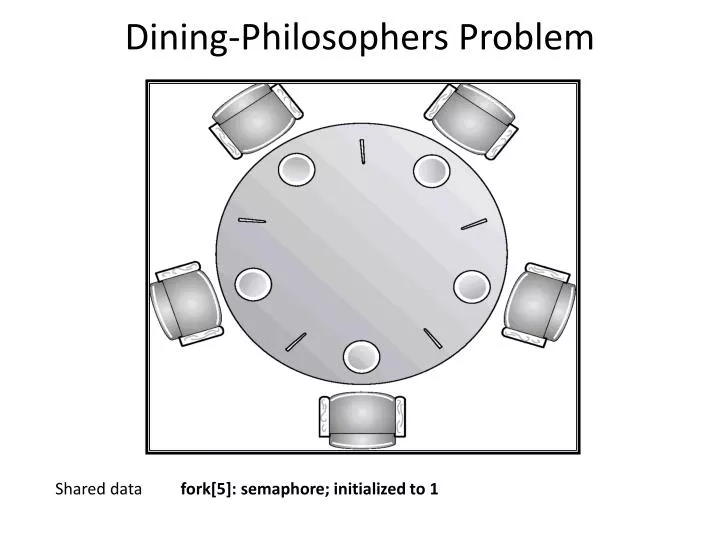
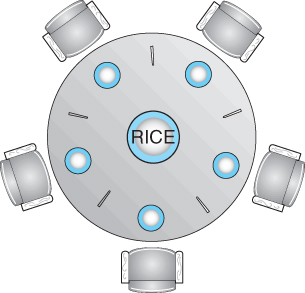
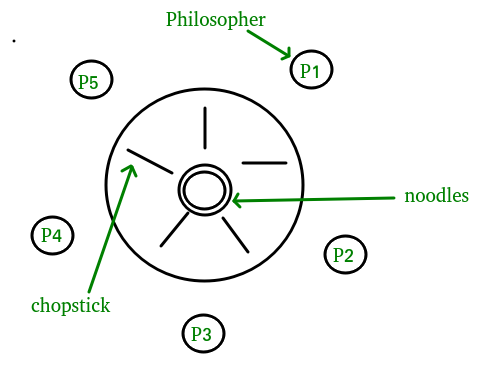
Explain dining philosophers problem in os. The dining philosophers problem states that there are 5 philosophers sharing a circular table and they eat and think alternatively. It only tells when to enter and exit the segment. A philosopher needs both their right and left chopstick to eat. Can suffer from deadlock e g.
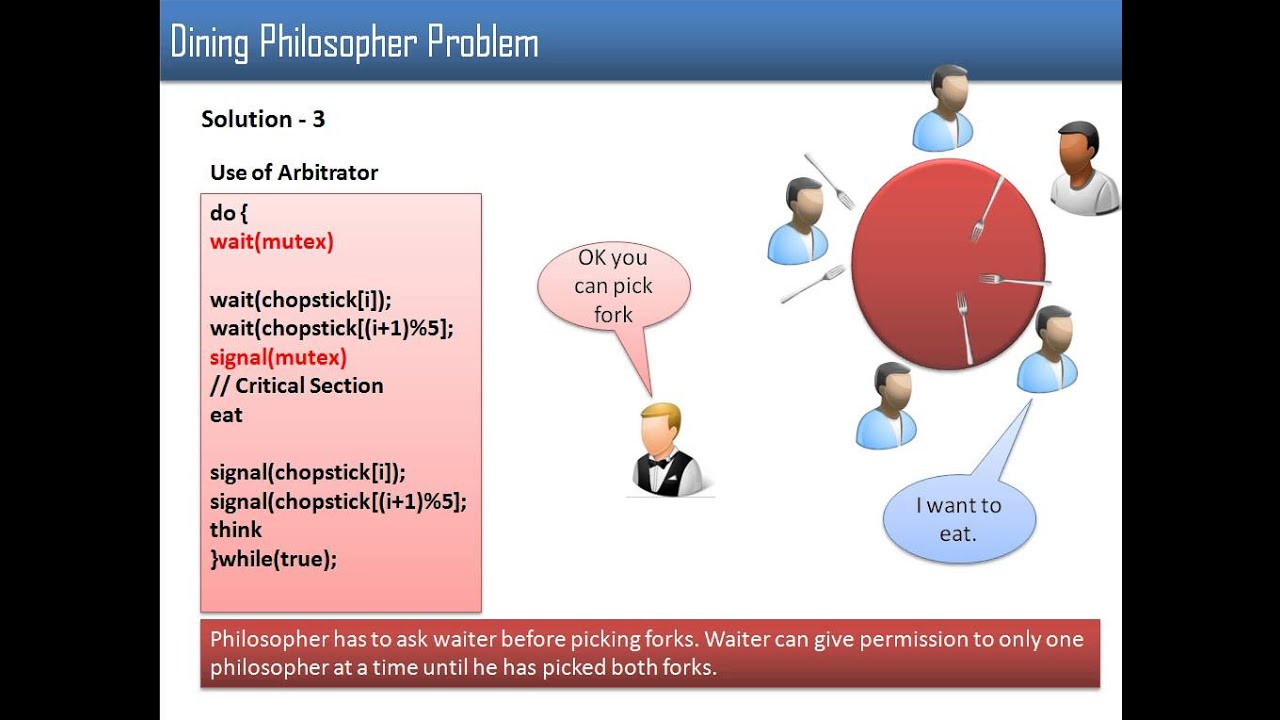
Monitor is used to control access to state variables and condition variables. Pick up both chopsticks in a critical section. Dining philosophers problem some deadlock free solutions. This requires protection of critical.
It was originally formulated in 1965 by edsger dijkstra as a student exam exercise presented in terms of computers competing for access to tape drive peripherals. Don t allow all philosophers to sit and eat think at once. Monitor based solution to dining philosophers. We illustrate monitor concepts by presenting a deadlock free solution to the dining philosophers problem.
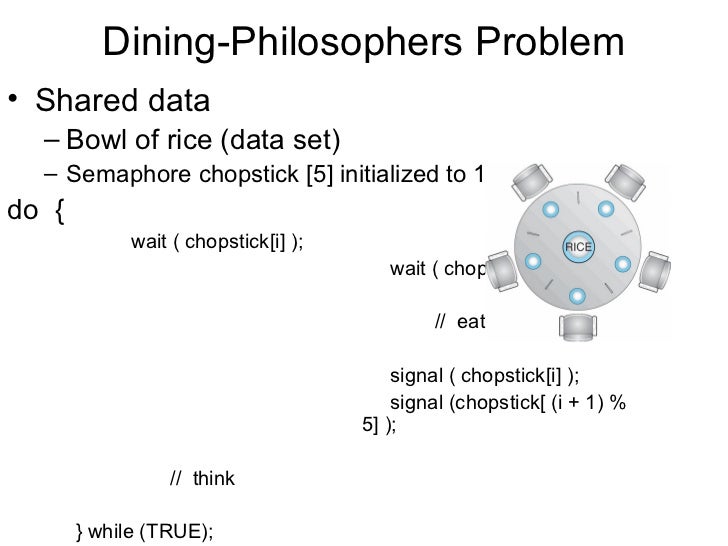
Allow at most 4 philosophers at the same table when there are 5 resources odd philosophers pick first left then right while even philosophers pick first right then left allow a philosopher to pick up chopsticks only if both are free. There is a bowl of rice for each of the philosophers and 5 chopsticks. Dining philosophers the dining philosophers problem is a classical synchronization problem. All philosophers decide to eat at the same time and all pick up their left chopstick first and or starvation some ways to avoid deadlock are.
The process of picking up chopsticks. A philosopher may eat if he can pickup the two chopsticks adjacent to him. Imagine for example an airline reservation system with many. In the dining philosopher problem we can implement an algorithm with mutexes that guarantee the philosophers not to be interrupted when they are changing their states e g.
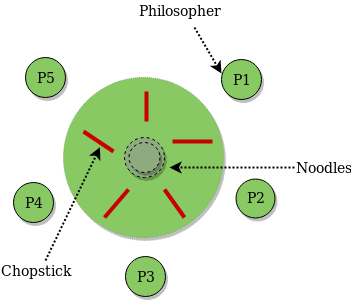
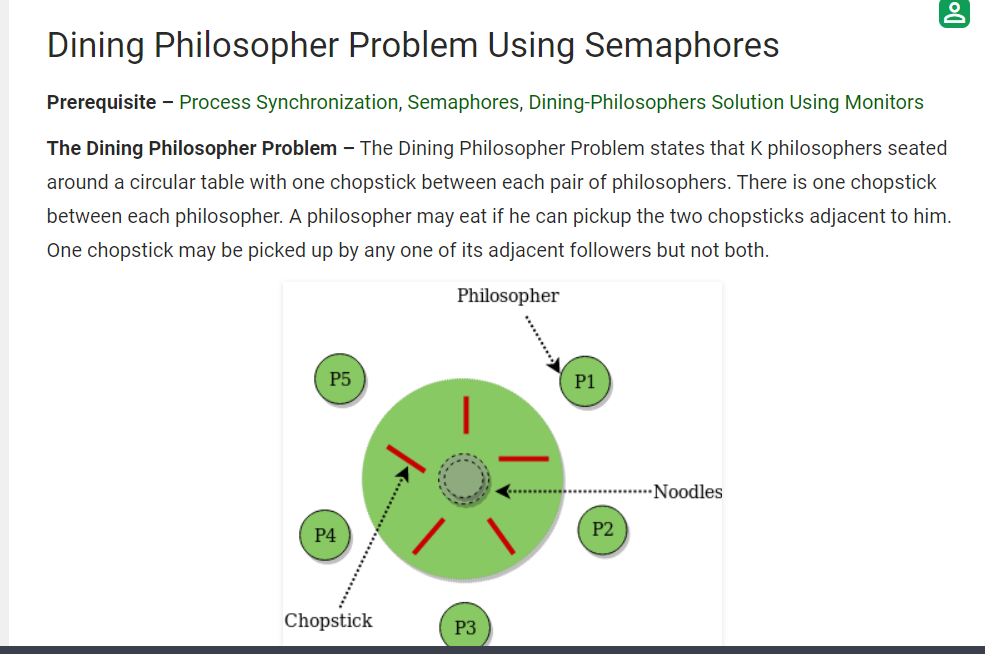
The book again chapter 6 has an excellent description of dining philosophers. Prerequisite process synchronization semaphores dining philosophers solution using monitors the dining philosopher problem the dining philosopher problem states that k philosophers seated around a circular table with one chopstick between each pair of philosophers. There is one chopstick between each philosopher. Another famous problem is the readers and writers problem which models access to a database courtois et al 1971.
Taken at face value it is a pretty meaningless problem but it is typical of many synchronization problems that you will see when allocating resources in operating systems.